AI and Current Applications in Corporate Real Estate
In our latest blog, we explore Neural Networks, AI, and their current applications in corporate real estate.

As we discussed in our last blog entry, artificial Intelligence (AI) is a broad field of computer science focused on creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. The technology has multiple subfields and, thus, many more applications. Today, we will take a deeper look at one field of AI, Neural Networks, and some of the existing applications of AI in corporate real estate.
Neural Networks
A neural network is a subset of Machine Learning inspired by the human brain's structure. A neural network consists of interconnected nodes (neurons) and is useful for image and speech recognition. A subset of neural networks is Deep Learning. These are neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks). While the image below might have only two layers, deep neural networks can have any number of layers and inputs.
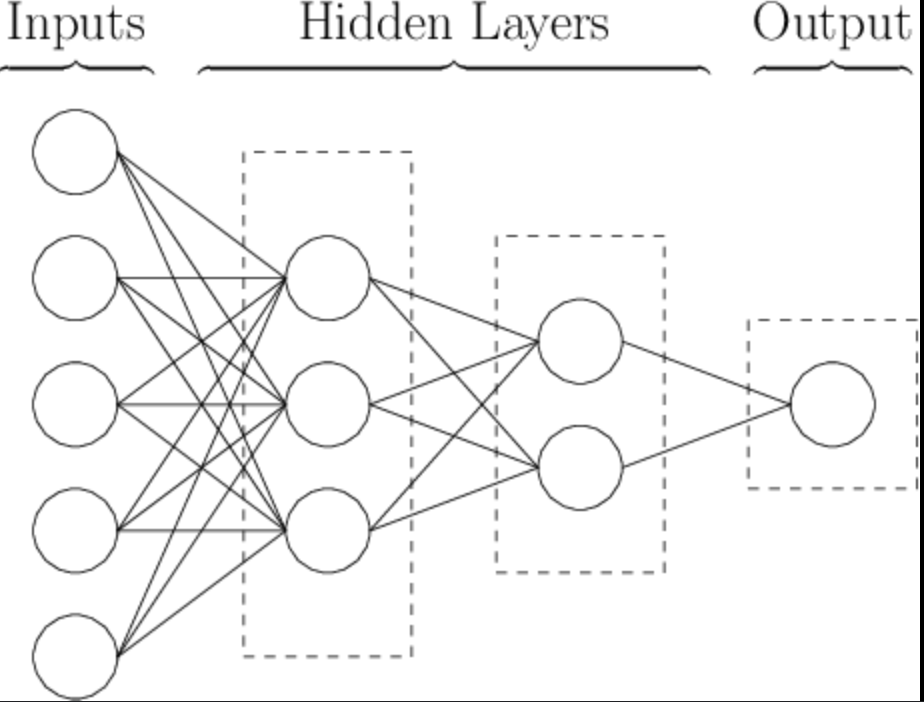
These kinds of artificial neural networks are useful for processing massive amounts of information and determining connections between different pieces of information that we might not have even thought to ask about. This can aid in predictive maintenance and thus result in cost savings on overall maintenance for real estate teams. This is just a single example. In reality, artificial neural networks alone have nearly unlimited use cases. It's all up to what you can imagine, kind of like our brains.
Applications of AI in Corporate Real Estate and Offices
Zooming back out from neural networks, we can understand that AI's capabilities can significantly enhance various aspects of corporate real estate (CRE) and office/facilities management (OM / FM). Below are some key ways this technology is already being applied today.
Data Analysis and Decision-Making
AI algorithms can be used for portfolio analytics to analyze vast amounts of data to predict trends and opportunities. This helps real estate teams make informed decisions and optimize their portfolio strategies.
Property Management
AI tools can automate the extraction and analysis of lease documents (lease abstraction), providing insights that can optimize portfolio management and operational efficiency. This task has been time-consuming for teams for decades, and one of the questions they often can't answer when a problem arises is, "What does it say in the lease?" Having searchable abstracts helps to alleviate the issue.
Space Utilization and Design
AI can analyze workspace usage patterns to optimize office layouts, ensuring efficient space use and simplifying space planning processes. It can also be used further in designing building interiors and layouts by generating multiple design options based on specific criteria, such as maximizing natural light, avoiding conflicts, or optimizing traffic flow. Tools have even been created to recognize conflicts in architectural plans in real time to speed up processes by understanding the legal codes of every jurisdiction in the U.S.
Security and Maintenance
As discussed in previous posts, these systems can predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance before issues arise, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. You can pair these systems with other sensors and automation to further enable your teams. In addition, AI-powered security solutions use biometric data to control access and enhance building security, making properties more secure. Facial recognition algorithms are already heavily used in many locations, from airports to secure facilities.
Stake Holder Engagement
Generative AI can create reports, such as executive summaries and portfolio reports, with customized dashboards for updating key stakeholders. This takes the pain out of what is an extremely repetitive task for most teams with an ever-changing list of KPIs to track. The team is also keenly tackling this at Trebellar.
Sustainability and Efficiency
AI can optimize energy usage in buildings, reducing costs and environmental impact. This includes smart systems that adjust lighting, heating, and cooling based on occupancy and usage patterns. It just doesn't make sense to run a building's lighting and cooling at 100% capacity with only 50% of the building filled. There's a better way, and teams are already adopting it.
Conclusion
As you can see, the practical applications of AI today are already wide-ranging. As the technologies that makeup AI continue to increase in adoption, more use cases will be created as well. Like we said, the only limitations are imagination and data. In our next blog, we'll dive into another field of AI and explain why data is so important for practical applications of AI, especially in corporate real estate.

